Get All Projects
Get a list of available projects for your organization.
GET /v1/projectsThe LoopFeed API provides programmatic access to content aggregation and publishing features. This documentation covers all available endpoints for getting all the projects for your organization, getting topics for a project, and retrieving published content.
Get All Projects
Get a list of available projects for your organization.
Get All Topics for a Project
Get a list of available topics for a project.
Get Published Content for a Topic
Retrieve the actual content items with filtering and pagination options for a topic.
All API requests are made to:
https://q.loop-feed.com/v1//v1/projects/.. API requests require authentication. Use X-Api-Key header to pass your API key.
X-Api-Key: <api-key>You can create the API key from LoopFeed dashboard. Navigate to “Settings” -> “API Keys” and click on “Create API Key”.
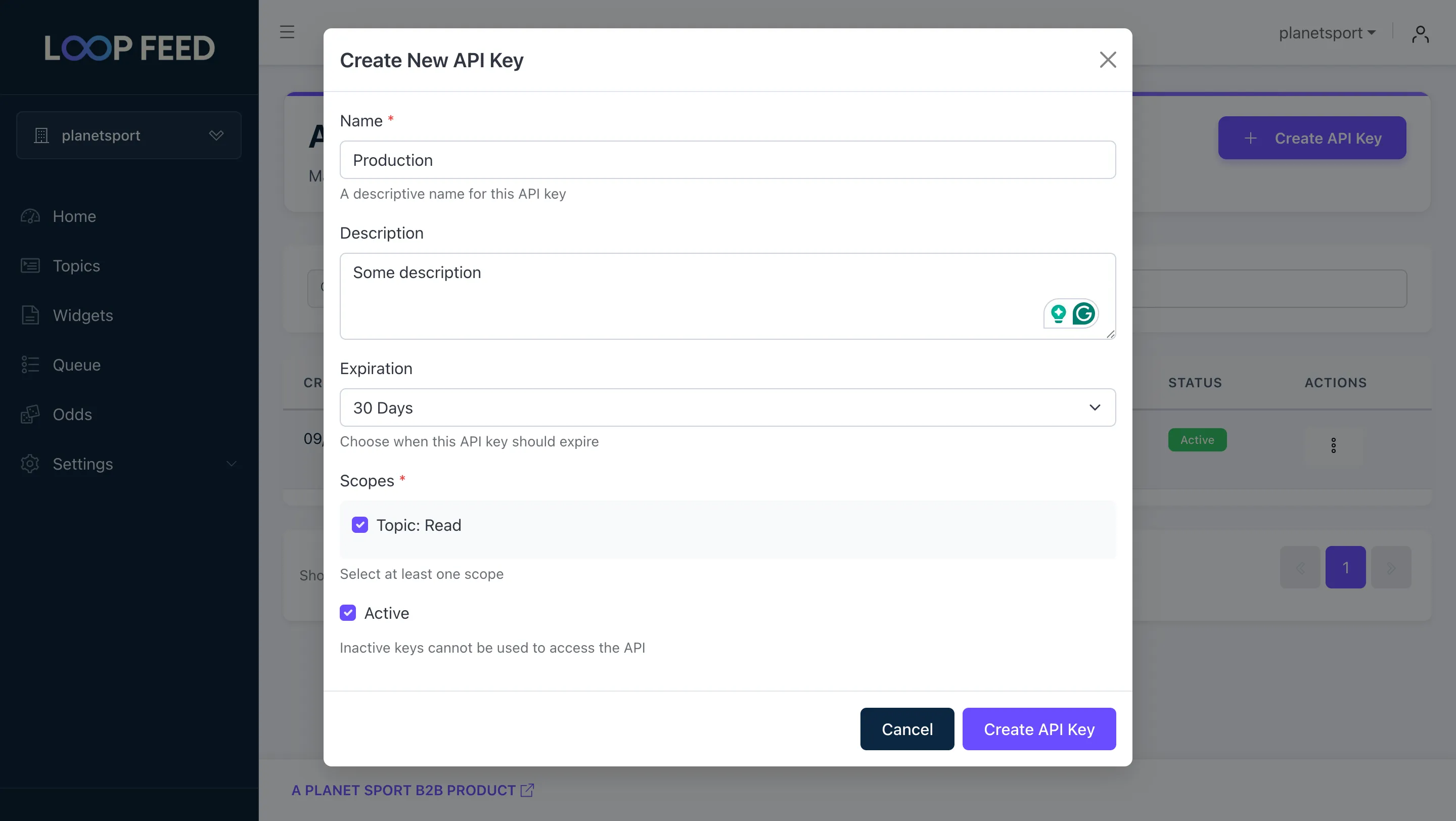
Generate the key with the default scopes and copy the key:
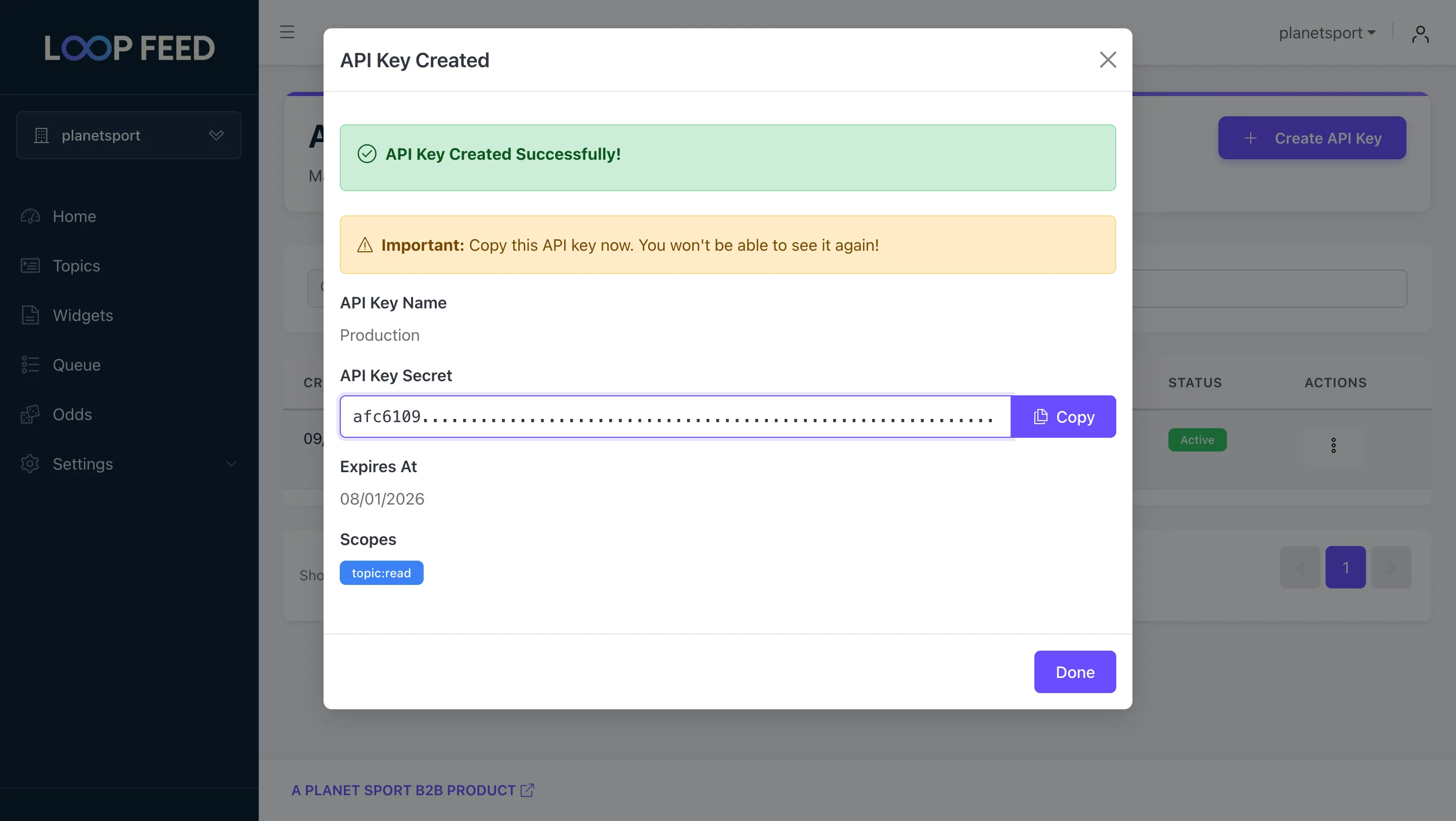
Use this key in the X-Api-Key header for all the protected endpoints.
Get All Projects
Get a list of available projects for your organization.
GET /v1/projectsGet All Topics for a Project
Get a list of available topics for a project.
GET /v1/project/<project-id>/topicsGet Published Content for a Topic
Retrieve the actual content items with filtering and pagination options for a topic.
GET /v1/topic/<topic-id>/contentGet Content Count (Deprecated)
Get the number of published content items for a topic.
GET /v1/topic/<topic-id>/countGet a list of all the projects for your organization. Projects are the top-level entities in LoopFeed and are used to group topics, widgets, queues etc.
GET https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/projects| Header | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
X-Api-Key | String | Required: Your API key |
[ { "id":"id-of-the-project", "name":"name-of-the-project" },]| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id | String | ID of the project |
name | String | Display name of the project |
Get a list of all the active topics for a specific project. Refer to the topic creation guide for more information on how to create and configure a topic.
GET https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/project/<project-id>/topics| Header | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
X-Api-Key | String | Required: Your API key |
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
project-id | String | Required: ID of the project |
[ { "id":"id-of-the-topic", "name":"name-of-the-topic", "url":"https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/content/id-of-the-topic", "metadata":null } ]| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id | String | ID of the topic |
name | String | Display name of the topic |
url | String | URL to fetch content for this topic |
metadata | Object | Metadata for the topic. |
Retrieve published content items for a specific topic. This is the main endpoint for getting actual content data.
GET https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/topic/<topic-id>/content| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
topic-id | String | Required: ID of the topic |
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
service | String | Optional: Filter by service (twitter, youtube, instagram, rss) |
since | Integer | Optional: Unix timestamp - content published after this time |
until | Integer | Optional: Unix timestamp - content published until this time |
limit | Integer | Optional: Number of results (default: 20) |
offset | Integer | Optional: Pagination offset (default: 0) |
[ { "id": "6fc9c511ab95bbd83f8478437a2f87ff1fc4f365", "service": "rss", "type": "link", "title": "Premier League fixture rescheduled", "text": "Our forthcoming Premier League fixture against Burnley has been rescheduled", "url": "https://www.arsenal.com/news/premier-league-fixture-rescheduled-0", "date": "2022-01-09T17:10:00.000Z", "author": { "name": "arsenal", "username": "arsenal" }, "media": [ { "type": "image", "url": "https://www.arsenal.com/sites/default/files/styles/desktop_16x9/public/images/DSC_2115_2021050642150098.JPG?itok=-0Af-IiL" } ], "kudos": { "score": 0, "rss_score": 0 }, "language": "en" }]| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id | String | Unique identifier for the content item |
service | String | Source platform (twitter, youtube, instagram, rss) |
type | String | Content type (video, image, link, status, embed, comment) |
title | String | Content title (may not be available for all content types) |
text | String | Content text/description (may contain HTML) |
tags | Array | Array of content tags |
url | String | URL to original content on source platform |
date | DateTime | Publication date in ISO 8601 format |
author | Object | Author information with name and username |
media | Array | Attached media (images, videos, embeds) |
kudos | Object | Engagement metrics (likes, shares, etc.) |
language | String | Content language (ISO 639-1 code) |
Get the number of published content items for a topic.
GET https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/topic/<topic-id>/count| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
topic-id | String | Required: ID of the topic |
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
service | String | Optional: Filter by service (twitter, youtube, instagram, rss) |
since | Integer | Optional: Unix timestamp - content published after this time |
until | Integer | Optional: Unix timestamp - content published until this time |
{ "count": 256}| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
count | Integer | Number of published content items for the topic |
Instead of using the count endpoint, fetch content directly with the since parameter:
// ❌ Old approach (deprecated)const countResponse = await fetch(`https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/topic/${topicId}/count?since=${lastFetchTimestamp}`);const { count } = await countResponse.json();if (count > 0) { const contentResponse = await fetch(`https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/topic/${topicId}/content?since=${lastFetchTimestamp}`); // ...}
// ✅ New approach (recommended)const contentResponse = await fetch(`https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/topic/${topicId}/content?since=${lastFetchTimestamp}`);const content = await contentResponse.json();// Process content directly - empty array means no new contentHere’s a complete example showing the recommended workflow for efficiently working with the LoopFeed API:
// 1. Get all projects for your organizationconst projectsResponse = await fetch('https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/projects', { headers: { 'X-Api-Key': 'your-api-key' } });const projects = await projectsResponse.json();
// Choose a project from the listconst projectId = projects[0].id; // Choose your project from the previous step
// 2. Get all active topics for the projectconst topicsResponse = await fetch(`https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/project/${projectId}/topics`, { headers: { 'X-Api-Key': 'your-api-key' } });const topics = await topicsResponse.json();
// Ideally, we should store all the projects and topics in a database here for later use.// You can have a cron job to fetch the projects and topics from the API.
// Choose a topic from the listconst topicId = topics[0].id; // Choose your topic from the previous step
// 3. Fetch content for the topicconst contentResponse = await fetch(`https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/topic/${topicId}/content`);const content = await contentResponse.json();
console.log('New content:');content.forEach(item => { console.log(`- ${item.service} ${item.type}: ${item.title}`);});
// 4. Update your last fetch timestamp (recommended)// You can store the last fetch timestamp in a database and use it to fetch only new content in subsequent requests.// saveLastFetchTimestamp(Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000));
// Subsequent requests should use the last fetch timestamp to fetch only new content.// const contentResponse = await fetch(`https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/topic/${topicId}/content?since=${lastFetchTimestamp}`);// const content = await contentResponse.json();
// console.log('New content:');// content.forEach(item => {// console.log(`- ${item.service} ${item.type}: ${item.title}`);// });For large result sets, use pagination:
async function fetchAllContent(topicId, since = null) { let allContent = []; let offset = 0; const limit = 100; // Maximum per request
while (true) { const response = await fetch(`https://q.loop-feed.com/v1/topic/${topicId}/content?limit=${limit}&offset=${offset}&since=${since}`); const content = await response.json();
if (content.length === 0) break; // No more content
allContent.push(...content); offset += limit;
// Break if we got less than the limit (last page) if (content.length < limit) break; }
return allContent;}Brand Toolkit
YouTube
Developer Guidelines
Brand Resources
When displaying content, ensure:
since parameter to fetch only new content since your last requestlimit values (100) to minimize request numbers